
Gastric Sleeve
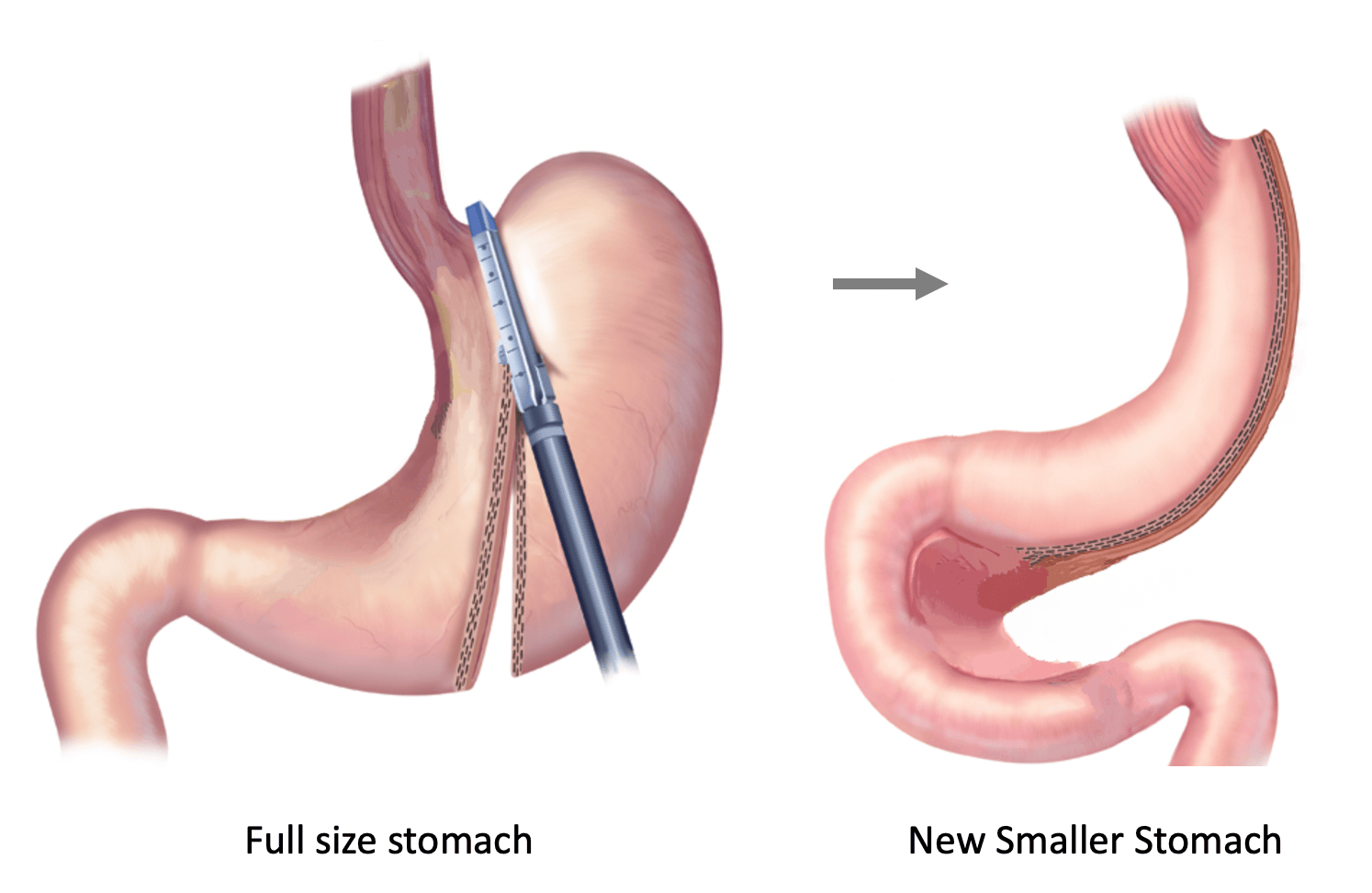
The Gastric Sleeve has become the most popular weight loss procedure over the last decade.
It is performed laparoscopically, using tiny skin incisions & a portion of the stomach is removed, leaving behind a smaller stomach about the size of a banana. This smaller stomach means you eat a smaller amount of food to feel full. Additionally, the part of the stomach that produces the hunger hormone Ghrelin is removed. This hormone plays a role in causing the feeling of hunger. After the Sleeve, as levels of Ghrelin decrease, and feeling of hunger decreases. Significantly less calories consumed leads to massive weight loss.
We find that patients are extremely satisfied with this procedure. They go about their daily lives with a stomach that still feels pretty normal, although significantly smaller. They still enjoy their favorite foods, and go to their favorite restaurants. Since there is no re-routing of intestines, there is minimal malabsorption of nutrients. It's a great operation, and can give fantastic long term results.
GUIDELINES FOR QUALIFYING WERE RECENTLY LOWERED- Recently Guidelines for this surgery have been lowered so many patients who may not have qualified before, can now have weight loss surgery with BMI as low as 30 for most people, and as low as 27 for asians.
INSURANCE COVERAGE - We’ll handle all the paperwork for approval.
SELF PAY- Our Self Pay fee for Gastric Sleeve starts at $13,990. Our very competitive package includes surgery, hospital fees, anesthesia, and one year of follow-ups. Generally, this procedure costs between $20-30k at other hospitals and bariatric programs.
FAST-TRACK - We can fast-track these procedures, especially for self-pay, since the insurance approval timing is eliminated, and you can have the procedure within a couple of weeks.
Gastric Sleeve
The Gastric Sleeve has risen to be the top weight loss surgery choice over the past ten years. This procedure, performed laparoscopically through small incisions, involves removing part of the stomach to leave a smaller, banana-sized pouch. This reduction in stomach size limits food intake and, importantly, removes the section that secretes Ghrelin, a hunger-inducing hormone. With lower Ghrelin levels, patients experience less hunger, consume fewer calories, and achieve significant weight loss.
Patients report high satisfaction with the Gastric Sleeve, enjoying a relatively normal but reduced stomach capacity. They continue to savor their favorite foods and dine out without the worry of severe nutrient malabsorption, thanks to the absence of intestinal rerouting. It's an effective surgery that, when performed on suitable candidates, delivers remarkable outcomes.
GUIDELINES FOR QUALIFYING WERE RECENTLY LOWERED- Recently Guidelines for this surgery have been lowered so many patients who may not have qualified before, can now have weight loss surgery with BMI as low as 30 for most people, and as low as 27 for asians.
INSURANCE COVERAGE - Insurances often cover this surgery if their guidelines are met. These guidelines are different amongst different insurance companies and hundreds of different plans. Our office will do all the work necessary to get you covered.
SELF PAY- Our lowest in North East price is $ 13,990 includes surgery fee, hospital OR fee, anesthesia fee, one overnight stay at the hospital, and 1 year of follow-ups (in-person or using tele-health) including dietary counseling. There are no hidden fees. Immediate appointments are available and you can have the surgery within weeks. Generally, this procedure costs between $20-30k elsewhere.
FAST-TRACK - We can fast-track these procedures, especially for self-pay, since the insurance approval timing is eliminated, and you can have the procedure within a couple of weeks.
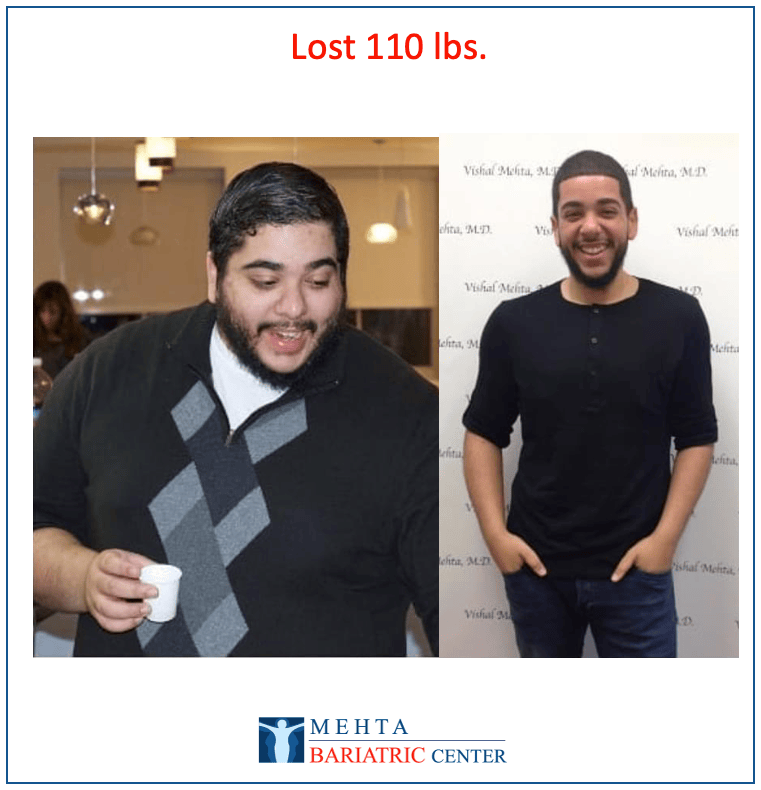
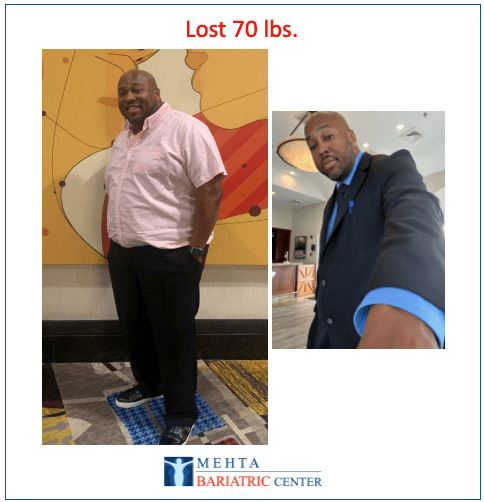
Meet some of Dr. Mehta’s patients who have experienced life-changing transformations. They now enjoy renewed health, confidence, and vitality after achieving their weight loss goals.
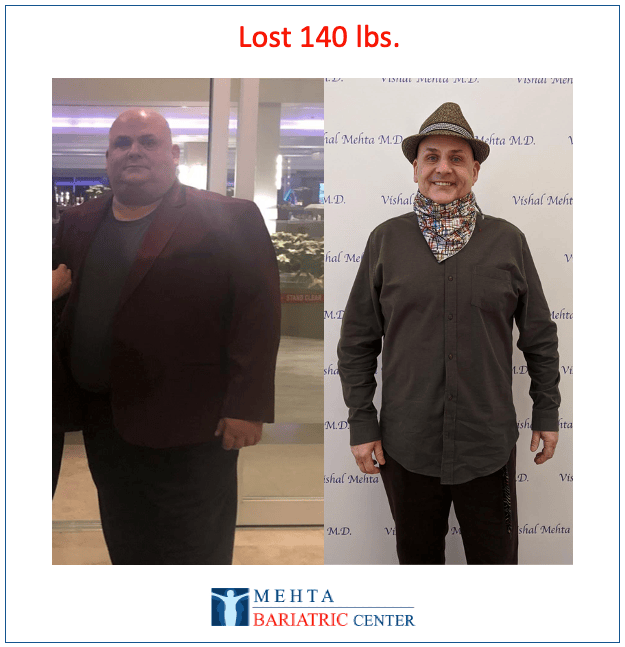
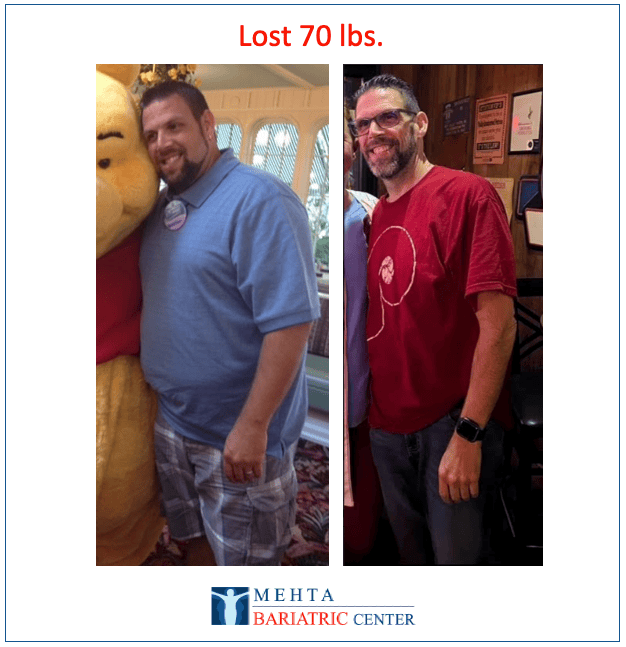
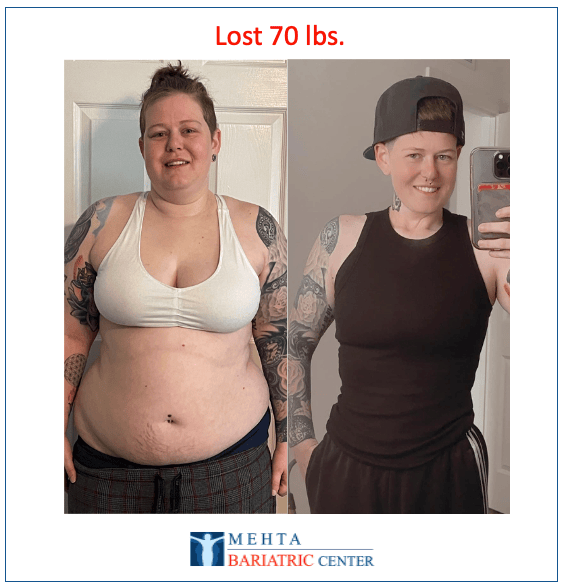
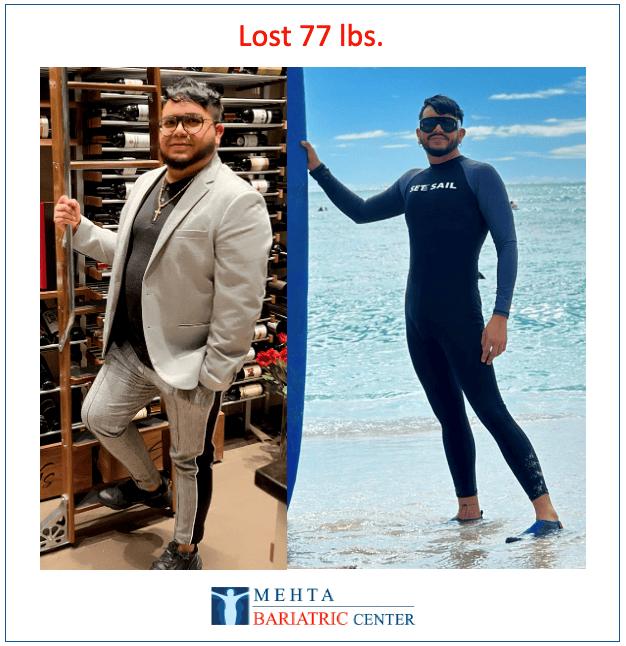
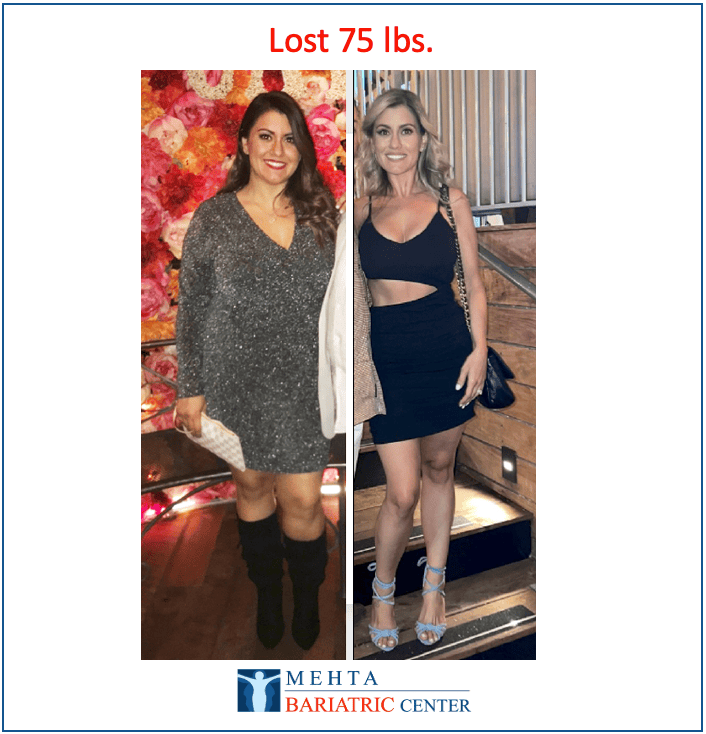
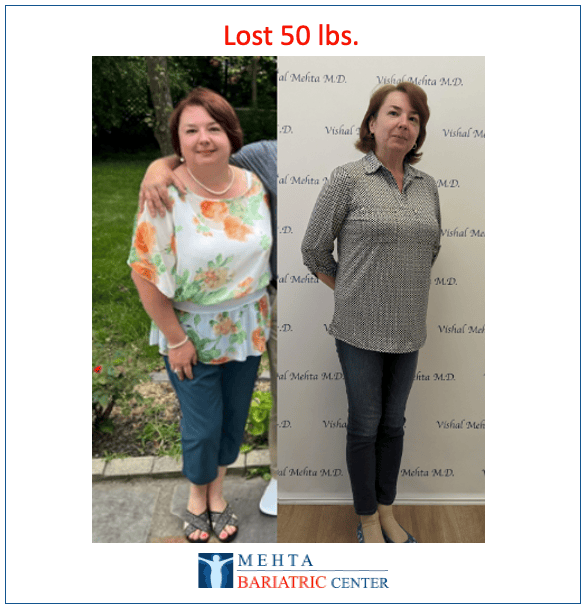
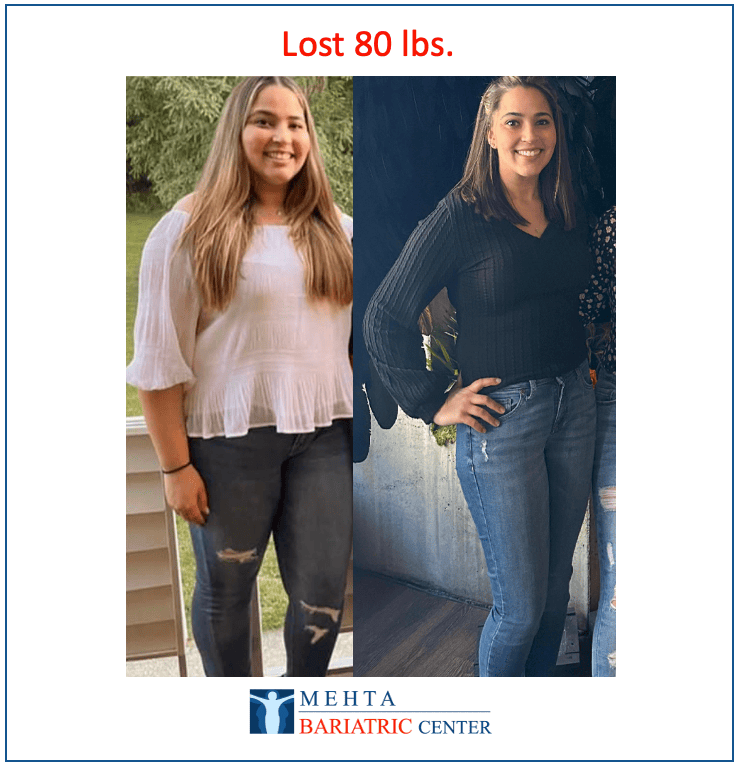

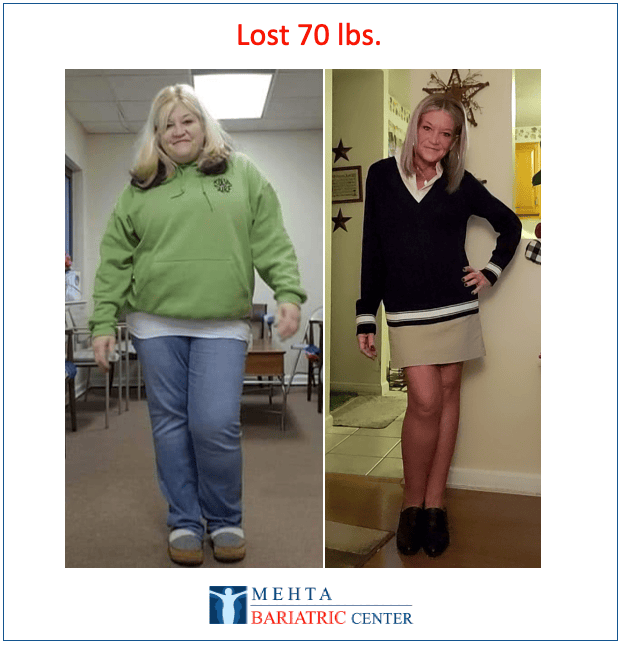












Meet some of our patients who have experienced life-changing transformations. They now enjoy renewed health, confidence, and vitality after achieving their weight loss goals.

















GASTRIC SLEEVE CAN SIGNIFICANTLY IMPROVE OR ERADICATE MANY MEDICAL CO-MORBIDITIES
Cardiovascular Disease
Type 2 Diabetes
Sleep Apnea
Joint Pain
Infertility Issues
Respiratory Issues
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Certain Cancers
Mental Health Issues
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Migraines
Fibromyalgia

SAFETY
Gastric Sleeve procedure have come a long way, and has become as safe as many routine surgeries. It's performed laparoscopically in a minimally invasive manner. Dr. Mehta has successfully performed thousands of weight loss surgeries over 2 decades, and continues to perform the entire surgery himself from beginning to end. These procedures have become significantly safer over the years, leading the American society of Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) to lower their guidelines to who can qualify for surgery.
You should also know that all surgeries are personally performed by Dr. Mehta, not by a junior surgeon. Students are never involved in surgery. You get the benefit of a highly trained and vastly experienced surgeon who has performed thousands of laparoscopic weight loss surgeries.
Weight Loss Surgery: Lowers Risk of death from HEART DISEASE by 40%, from DIABETES by 92% & from CANCER by 60%
HOW MUCH WEIGHT WILL I LOSE?
Overall weight loss depends on many factors. Since you are unique, and so is your weight loss journey, diet & lifestyle, how much weight you will lose can only be estimated after putting your entire picture together regarding your age, height, weight, medical illnesses, and lifestyle. Smaller patients can lose around 50 lbs. but larger ones can lose up to 180 lbs. or more. Results vary based on many factors such as age, sex, and conforming with proper post-op nutrition guidelines. The size of the gastric sleeve can be customized for the desired weight loss whether you want to lose 50 lbs. or 150.
HOW MUCH TIME OFF IS NEEDED?
Nearly all of our patients go home after 1 overnight stay at the hospital. Most people can resume work from home in 3 days or go to a desk job in about 7 days.
IS IT SAFE ?
SAFETY
Gastric Sleeve procedure have come a long way, and has become as safe as many routine surgeries. It's performed laparoscopically in a minimally invasive manner. Dr. Mehta has successfully performed thousands of weight loss surgeries over 2 decades, and continues to perform the entire surgery himself from beginning to end. These procedures have become significantly safer over the years, leading the American society of Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) to lower their guidelines to who can qualify for surgery.
You should also know that all surgeries are personally performed by Dr. Mehta, not by a junior surgeon. Students are never involved in surgery. You get the benefit of a highly trained and vastly experienced surgeon who has performed thousands of laparoscopic weight loss surgeries.
Weight Loss Surgery: Lowers Risk of death from HEART DISEASE by 40%, from DIABETES by 92% & from CANCER by 60%
HOW MUCH WEIGHT WILL I LOSE?
Overall weight loss depends on many factors. Smaller patients can lose around 50 lbs. but larger ones can lose up to 180 lbs. or more. Results vary based on many factors such as age, sex, and conforming with proper post-op nutrition guidelines. The size of the gastric sleeve can be customized for the desired weight loss whether you want to lose 50 lbs. or 180.
HOW MUCH TIME OFF IS NEEDED?
Nearly all of our patients go home after 1 overnight stay at the hospital. Most people can resume work from home in 3 days or go to a desk job in about 7-10 days. Those who can take more time off, generally take 2 weeks.
INSURANCE COVERAGE
DOES INSURANCE COVER THE GASTRIC SLEEVE ?
Insurance companies can be complex and benefits frequently change. We would be glad to check your coverage at no cost, and do all the leg-work to acquire insurance approval.
IF INSURANCE DOESN'T COVER SURGERY, WHAT ARE MY OPTIONS?
1. Options include upgrading insurance. You can contact us and find out which insurance benefits would best fit you.
2. Self-Pay. Our self-pay fees for Gastric Sleeve are the lowest around despite the fact that we spare no operative expense and use the best surgery devices and materials on the planet, for the added safety of all our patients. Our current package price is $13,990 and includes surgery fee, hospital OR fee, anesthesia fee, one overnight stay at the hospital, and 1 year of follow-ups (in-person or using tele-health) including dietary counseling. Immediate appointments are available and you can have the surgery within weeks. Generally, this procedure costs between $20-30k elsewhere.
3. Our office can sometimes get insurances to cover part of the procedure.
4. Financing is available using Care Credit and Health Care Services Loans.
DOES INSURANCE COVER THE GASTRIC SLEEVE ?
Insurance companies can be complex and benefits frequently change. We would be glad to check your coverage at no cost, and do all the leg-work to acquire insurance approval.
IF INSURANCE DOESN'T COVER SURGERY, WHAT ARE MY OPTIONS?
1. Options include upgrading insurance. You can contact us and find out which insurance benefits would best fit you.
2. Self-Pay. Our self-pay fees for Gastric Sleeve are the lowest around despite the fact that we spare no operative expense and use the best surgery devices and materials on the planet, for the added safety of all our patients. Our current package price is very competitive and includes surgery fee, hospital OR fee, anesthesia fee, one overnight stay at the hospital, and 1 year of follow-ups (in-person or using tele-health) including dietary counseling. Immediate appointments are available and you can have the surgery within weeks. Generally, this procedure costs between $20-30k elsewhere. We have better options.
3. Our office can sometimes get insurances to cover part of the procedure.
4. Financing is available using Care Credit and Health Care Services Loans.
DOES INSURANCE COVER THE GASTRIC SLEEVE ?
Insurance companies can be complex and benefits frequently change. We would be glad to check your coverage at no cost, and do all the leg-work to acquire insurance approval.
IF INSURANCE DOESN'T COVER SURGERY, WHAT ARE MY OPTIONS?
1. Options include upgrading insurance. You can contact us and find out which insurance benefits would best fit you.
2. Self-Pay. Our self-pay fees for Gastric Sleeve are the lowest around despite the fact that we spare no operative expense and use the best surgery devices and materials on the planet, for the added safety of all our patients. Our current package price is very competitive and includes surgery fee, hospital OR fee, anesthesia fee, one overnight stay at the hospital, and 1 year of follow-ups (in-person or using tele-health) including dietary counseling. Immediate appointments are available and you can have the surgery within weeks. Generally, this procedure costs between $20-30k elsewhere. We have better options.
3. Our office can sometimes get insurances to cover part of the procedure.
4. Financing is available using Care Credit and Health Care Services Loans.
WHAT OUR PATIENTS ARE SAYING
"Dr. Mehta has given me my life back! I am able to live and work like I did when I was young! I feel I was given a chance to start over and I owe it to Dr. Mehta. My surgery was flawless. I felt great after. Recovery was quick and now I am on my way to new goals. Thank you so much for the new LIFE!!"
Gary G. Franklin Park, NJ
"I suffered from diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, sleep apnea, lack of energy, swollen feet and grumpiness. Best of all I no longer use medicines & no longer suffer from any of the other medical issues. Even my grumpiness has gone away. My PCP was amazed and very impressed. I wish that there was a way to thank Dr. Mehta for what he has done. If I could do it all over again, I would in heart beat with Dr. Mehta."
-Miguel C, Bordentown, NJ
WHAT OUR PATIENTS ARE SAYING
"I was made aware of Dr. Mehta’s program through an associate at work. I was shocked at the reaction that Dr. Mehta received from his patients during the seminar. He answered all of my questions straight to the point. My total experience with the program was fantastic!! Dr. Mehta has given me my life back! I am able to live and work like I did when I was young! I feel I was given a chance to start over and I owe it to Dr. Mehta. My surgery was flawless. I felt great after. Recovery was quick and now I am on my way to new goals. Thank you so much for the new LIFE!!"
GARY G. FRANKLIN PARK, NJ
"I suffered from diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, sleep apnea, lack of energy, swollen feet and grumpiness. Best of all I no longer use medicines & no longer suffer from any of the other medical issues. Even my grumpiness has gone away. My PCP was amazed and very impressed. I wish that there was a way to thank Dr. Mehta for what he has done. If I could do it all over again, I would in heart beat with Dr. Mehta."
Miguel C. (Lost 76 lbs.)
WHAT OUR PATIENTS ARE SAYING
Gary G. Franklin Park, NJ
-Miguel C, Bordentown, NJ
"I was made aware of Dr. Mehta’s program through an associate at work. I was shocked at the reaction that Dr. Mehta received from his patients during the seminar. He answered all of my questions straight to the point. My total experience with the program was fantastic!! Dr. Mehta has given me my life back! I am able to live and work like I did when I was young! I feel I was given a chance to start over and I owe it to Dr. Mehta. My surgery was flawless. I felt great after. Recovery was quick and now I am on my way to new goals. Thank you so much for the new LIFE!!"
GARY G. FRANKLIN PARK, NJ
"I suffered from diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, sleep apnea, lack of energy, swollen feet and grumpiness. Best of all I no longer use medicines & no longer suffer from any of the other medical issues. Even my grumpiness has gone away. My PCP was amazed and very impressed. I wish that there was a way to thank Dr. Mehta for what he has done. If I could do it all over again, I would in heart beat with Dr. Mehta."
- Miguel C. (Lost 76 lbs.)
Discover why over 4,000 individuals have entrusted us with their transformative journeys:
Discover why over 4,000 individuals have entrusted us with their transformative journeys:
PRINCETON, NJ OFFICE
1 Academy Street, Princeton, NJ 08540
OLD BRIDGE, NJ OFFICE
2 Hospital Plaza, Suite 470, Old Bridge, NJ
Serving NJ, PA & NY
Call/Text (609)924-0200
Call: 888-NEW-BODY
"I was made aware of Dr. Mehta’s program through an associate at work. I was shocked at the reaction that Dr. Mehta received from his patients during the seminar. He answered all of my questions straight to the point. My total experience with the program was fantastic!! Dr. Mehta has given me my life back! I am able to live and work like I did when I was young! I feel I was given a chance to start over and I owe it to Dr. Mehta. My surgery was flawless. I felt great after. Recovery was quick and now I am on my way to new goals. Thank you so much for the new LIFE!!"
GARY G. FRANKLIN PARK, NJ
"I suffered from diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, sleep apnea, lack of energy, swollen feet and grumpiness. Best of all I no longer use medicines & no longer suffer from any of the other medical issues. Even my grumpiness has gone away. My PCP was amazed and very impressed. I wish that there was a way to thank Dr. Mehta for what he has done. If I could do it all over again, I would in heart beat with Dr. Mehta."
- Miguel C. (Lost 76 lbs.)
